Cloud Penetration Testing: Securing Your Cloud Infrastructure

Introduction
Understanding Cloud Penetration Testing
The Need for Cloud Penetration Testing
As cloud computing offers numerous benefits, it also introduces unique security challenges. Some of the key factors that highlight the need for cloud penetration testing are:
-
Shared Responsibility Model — Cloud service providers (CSPs) follow a shared responsibility model, where they are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, and configurations. Cloud pentesting helps businesses fulfill their security responsibilities effectively.
-
Evolving Threat Landscape — Cyber threats are continually evolving, and cloud environments are no exception. Regular cloud pentesting enables organizations to stay ahead of potential attackers and protect their cloud-based assets from new and emerging threats.
-
Compliance Requirements — Many industries and regulatory bodies have specific security and compliance standards that organizations must adhere to when using cloud services. Cloud penetration testing helps meet these requirements and demonstrates a commitment to security.
-
Data Breach Prevention — Data breaches can be costly and damaging to an organization’s reputation. Cloud pentesting assists in identifying and resolving security gaps before they are exploited by malicious actors.
Cloud Penetration Testing Components
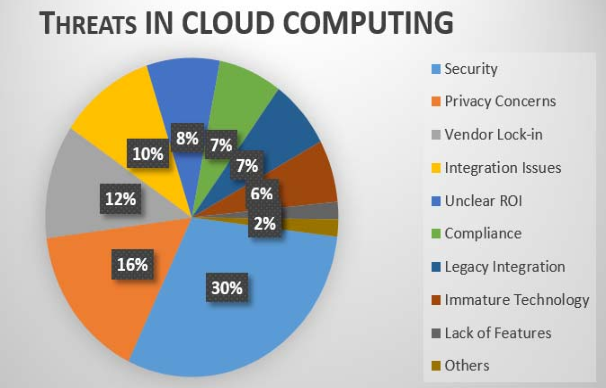
A comprehensive cloud penetration testing approach encompasses various components to ensure a thorough assessment of the cloud environment:
-
Cloud Architecture Review — Before initiating cloud pentesting, it is essential to review the cloud architecture, including network configurations, access controls, identity and access management (IAM) policies, and data storage. This review provides crucial insights into potential entry points for attackers and helps tailor the testing scope accordingly.
-
Web Application Testing — For cloud-based applications, web application testing is crucial. Testers assess the security of web applications hosted in the cloud, looking for common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), and insecure direct object references.
-
Network Vulnerability Assessment — Conducting network vulnerability assessments on cloud-based networks helps identify weak points in the network infrastructure, including exposed ports, misconfigured firewalls, and potential avenues for lateral movement.
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM) Testing — IAM testing evaluates the cloud environment’s access control mechanisms, verifying that only authorized users have access to sensitive resources. It includes testing for privilege escalation, weak passwords, and misconfigured IAM policies.
-
Data Security Assessment — Data is a valuable asset for any organization, and cloud pentesting should include an assessment of data security measures. This involves ensuring data encryption in transit and at rest, as well as evaluating access controls to prevent unauthorized data exposure.
-
API Security Testing — If the cloud environment relies on APIs for communication between services, API security testing becomes crucial. Testers identify vulnerabilities in the API endpoints, authentication mechanisms, and data validation procedures.
-
Container Security Testing — In containerized cloud environments, testers assess container security to prevent container breakouts and privilege escalation. This includes reviewing container configurations, container orchestration, and container image security.
-
Cloud Storage Security — Cloud storage is a common target for attackers, making it essential to test the security of data stored in cloud storage services. Assessing access controls and encryption mechanisms helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Common Cloud Vulnerabilities

Several vulnerabilities are commonly found in cloud environments. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for organizations to focus their cloud penetration testing efforts effectively.
Some common cloud vulnerabilities include —
-
Insecure API Endpoints — Improperly secured API endpoints can lead to unauthorized access and data exposure.
-
Weak Authentication — Weak passwords or misconfigured authentication mechanisms can compromise user accounts and lead to unauthorized access.
-
Privilege Escalation — Inadequate access controls may allow attackers to escalate privileges and gain unauthorized administrative rights.
-
Insecure Data Storage — Improperly configured cloud storage may lead to data exposure, allowing unauthorized users to access sensitive information.
-
Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR) — Lack of proper validation and authorization checks can enable attackers to access unauthorized resources.
-
Denial of Service (DoS) — A successful DoS attack can disrupt cloud services and cause service unavailability.
More on OWASP Cloud TOP 10 Link
Cloud Penetration Testing Tools
To conduct effective cloud penetration testing, security professionals rely on a variety of specialized tools. Some popular cloud pentesting tools include:
-
OWASP ZAP — An open-source security tool with API testing capabilities. It is used for manual and automated testing of cloud APIs.
-
Burp Suite — A web application security tool that includes features for cloud web application testing.
-
Metasploit — A widely-used penetration testing framework that includes modules for cloud environments.
-
AWS CLI — Command-line interface for Amazon Web Services (AWS) that allows testers to interact with AWS services for security assessment.
-
Pacu — Pacu, short for “Policy as Code Utility,” is an open-source AWS exploitation framework designed for cloud security testing. It automates the process of assessing AWS environments and identifying potential vulnerabilities related to misconfigurations and security best practices.
-
CloudMapper — CloudMapper is a powerful tool for visualizing and assessing AWS cloud environments. It helps identify potential security risks, including overly permissive IAM policies, open security groups, and potential data exposure points.
-
Scout Suite — Scout Suite is an open-source multi-cloud security auditing tool that supports AWS, Azure, and GCP. It provides comprehensive security assessments, including identity management, storage, networking, and compliance.
Best Practices for Cloud Penetration Testing
To derive maximum value from cloud penetration testing, organizations should follow best practices:
-
Engage Certified Professionals — Cloud penetration testing requires specialized skills and knowledge. Engage certified professionals or reputable third-party security firms with experience in cloud security testing to ensure accurate and comprehensive assessments.
-
Collaborate with Cloud Service Providers — Work closely with your cloud service providers to understand their security policies, processes, and compliance standards. Ensure that the cloud penetration testing aligns with the CSP’s guidelines to avoid any service interruptions.
-
Scope and Objectives — Clearly define the scope and objectives of the cloud penetration testing exercise. Tailor the testing approach based on the cloud environment’s complexity and critical assets.
-
Test Regularly and Proactively — Cloud environments are dynamic, and security risks can change rapidly. Regular and proactive cloud pentesting ensures ongoing security and helps detect vulnerabilities as soon as they emerge.
-
Risk Prioritization — Assess and prioritize the identified vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact on the cloud environment. Address high-risk issues promptly to minimize the chances of exploitation.
-
Documentation and Reporting — Maintain comprehensive documentation throughout the cloud penetration testing process. The final report should include detailed findings, recommended remediation steps, and a roadmap for improving cloud security.
-
Continuous Improvement — Use the insights gained from cloud penetration testing to enhance the security posture continuously. Apply the lessons learned to strengthen security controls and prevent similar vulnerabilities in the future.
